Published: 27 January 2026
Investment property is one of the most commonly misunderstood areas of financial reporting — especially for growing businesses, property investors, and groups holding mixed-use assets.
IAS 40 – Investment Property sets out how certain land and buildings should be recognised, measured, and disclosed under IFRS. Getting this right is critical, as the accounting treatment can materially affect profits, equity, and key performance ratios.
At Direct Assist, we help clients apply IFRS standards clearly and consistently. Below is a practical breakdown of IAS 40, without the jargon overload.
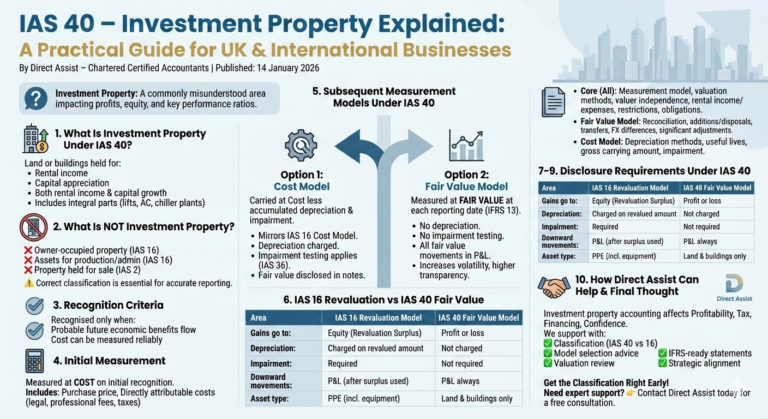
Under IAS 40, investment property is defined as land or buildings (or part of a building) that are:
Held to earn rental income, or
Held for capital appreciation, or
Held for both rental income and capital growth
This includes integral parts of a building, such as lifts, air-conditioning systems, and chiller plants.
IAS 40 specifically excludes the following assets:
Owner-occupied property
→ Accounted for under IAS 16 – Property, Plant and Equipment
Assets used in production, supply of goods or services, or administration
→ Also covered by IAS 16
Property held for sale in the ordinary course of business
→ Accounted for under IAS 2 – Inventories
Correct classification at the outset is essential — misclassification can lead to incorrect profits and audit issues.
An investment property is recognised only when both conditions are met:
It is probable that future economic benefits will flow to the entity, and
The cost of the property can be measured reliably
If either condition is not met, the property cannot be recognised under IAS 40.
On initial recognition, investment property is measured at cost.
This includes:
Purchase price
Directly attributable costs (legal fees, professional fees, transfer taxes, etc.)
After initial recognition, IAS 40 allows two accounting models. The chosen model must be applied consistently to all investment properties.
Option 1: Cost Model
Under the cost model, investment property is carried at:
Cost
less accumulated depreciation
less accumulated impairment losses
This approach mirrors the cost model used in IAS 16.
Key points:
Depreciation is charged
Impairment testing applies (IAS 36)
Fair value is disclosed in the notes (where reliably measurable)
Under the fair value model, investment property is measured at fair value at each reporting date, in line with IFRS 13 – Fair Value Measurement.
Key features:
No depreciation is charged
No impairment testing is required
All fair value movements (upward and downward) are recognised directly in profit or loss
This model can significantly increase profit volatility — but provides greater transparency for investors.
Although they sound similar, these models are fundamentally different:
| Area | IAS 16 Revaluation Model | IAS 40 Fair Value Model |
|---|---|---|
| Where gains go | Equity (Revaluation Surplus) | Profit or Loss |
| Depreciation | Charged on revalued amount | Not charged |
| Impairment testing | Required | Not required |
| Downward movements | P&L (after surplus used) | P&L always |
| Asset type | PPE (incl. equipment) | Land & buildings only |
Understanding this distinction is critical when groups hold both owner-occupied and investment properties.
Measurement model used (cost or fair value)
Valuation methods and key assumptions
Whether valuations were performed by independent qualified valuers
Rental income from investment property
Direct operating expenses related to rental income
Restrictions on property use or income remittance
Contractual obligations for acquisition, development, or maintenance
Entities using the fair value model must also disclose:
Reconciliation of carrying amounts from beginning to end of the period
Additions, disposals, and fair value movements
Transfers to/from inventories or owner-occupied property
Foreign exchange differences
Significant adjustments to external valuations
Cases where cost model is used for specific properties despite overall fair value approach
Entities using the cost model must disclose:
Depreciation methods applied
Useful lives or depreciation rates
Gross carrying amount and accumulated depreciation
Impairment losses recognised or reversed
Detailed reconciliation of carrying amounts during the period
Investment property accounting can materially affect:
Profitability
Tax planning
Financing covenants
Investor confidence
At Direct Assist, we support businesses by:
✅ Assessing correct classification under IAS 40 vs IAS 16
✅ Advising on cost vs fair value model selection
✅ Reviewing valuation assumptions and disclosures
✅ Ensuring IFRS and audit-ready financial statements
✅ Aligning accounting treatment with tax and commercial strategy
IAS 40 is not just about valuation — it’s about presenting the economic reality of your property holdings.
Ask yourself:
Are all properties correctly classified?
Is your measurement model aligned with your business strategy?
Would an investor clearly understand how property values affect profits?
If you’re unsure, now is the time to review.
👉 Contact Direct Assist today for a free consultation or instant online quote.
Direct Assist – Chartered Certified Accountants helping businesses report with clarity and confidence.
Excellent rating
Based on 84 reviews
(0203) 633 2018
info@directassistaccountants.co.uk
Provide your details and one of our experts will be in touch.